有機半導体
Organic Semiconductors
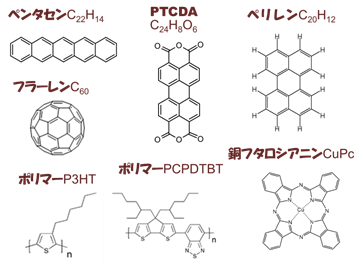
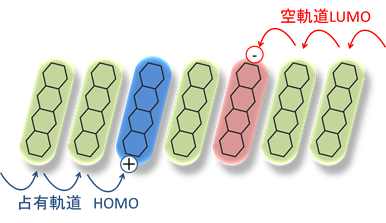
有機半導体分子の例を挙げます。これらの分子の特徴は、π軌道が大きく広がっていることです。このため、これらの分子が集合した固体では、軌道と軌道の重なりを通じて電気が流れるわけです。半導体中では、正の電荷をもつホール(正孔)と負の電荷をもつ電子が電気の流れを担います。ホールは最高被占軌道(Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital: HOMO)、電子は最低空軌道( Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital; LUMO)を通じて流れます。これらHOMO、LUMOの軌道エネルギーや分子軌道の重なりを調べることが、有機半導体の電気伝導を考える上で重要であることがわかると思います。軌道エネルギーは電子分光法などの実験手法により調べます。一方、分子軌道の重なりは、分子軌道の形と有機半導体の固体構造に影響されます。このようなことから、電子分光法による研究とさまざまな手法による薄膜構造・分子配向の研究を進めています。
Organic semiconducting molecules are characterized by extended pi-orbitals through which the intra-molecular charge transport occurs. The holes and electrons move through the overlap of highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO)and lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), respectively. We are, therefore, interested in energies and shapes of molecular orbitals in solids as well as geometric structures of and molecular orientation in organic solids.